Last Updated on July 15, 2023 by admin
| HTTP | HTTPS |
| It is a hypertext transfer protocol. It is less secure as the data can be vulnerable to hackers. | It’s a hypertext transfer protocol with encryption. It is designed to prevent hackers from accessing critical information. It is secure against such attacks. |
| It uses port 80 by default | It uses port 443 by default. |
| It’s a bad choice for today’s use. | If the website needs to collect private information such as credit card numbers, then it is a must-have protocol. |
| It operates at the TCP/IP level | HTTPS doesn’t have any separate protocol. It operates using HTTP but uses an encrypted TLS/SSL protocol. |
| HTTP does not improve search rankings | HTTPS helps to improve search ranking. |
| Vulnerable to hackers | It is highly secure as the data is encrypted before it’s sent across the network. |
Introduction
Secure your website with an SSL/TLS certificate to enhance security and credibility. In this blog post, we’ll explore the differences between HTTP and HTTPS and discuss the pros and cons of each protocol.
What is HTTP?
HTTP, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is a protocol for transferring data over the internet. When you enter a URL into your web browser and press “enter,” your browser sends a request to the server hosting the website for its content. The server then responds by sending the requested content back to your browser to display the website.
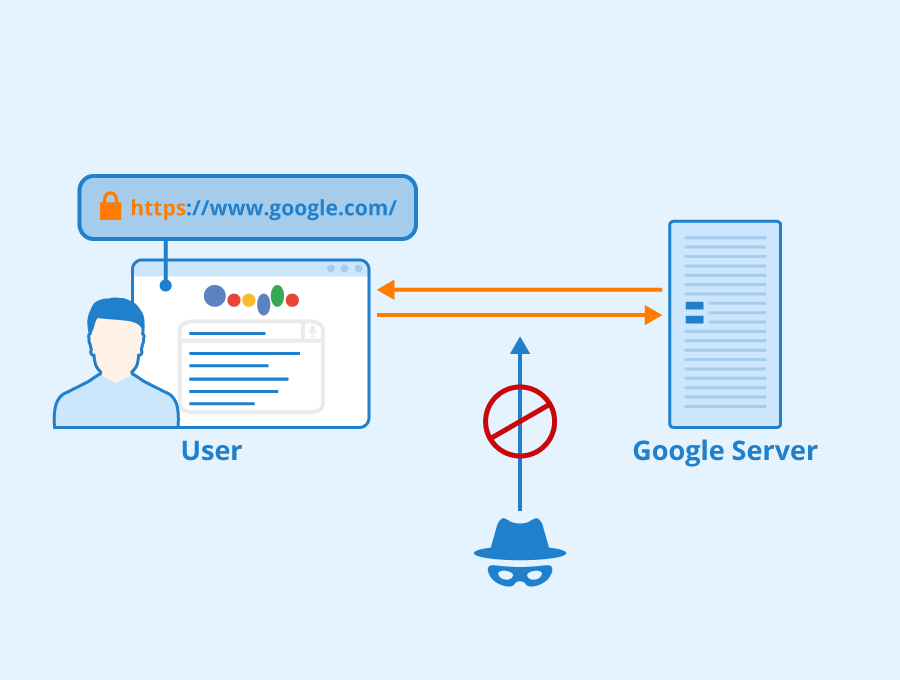
HTTP is a simple, stateless protocol that transmits data in plaintext, meaning the data is not encrypted and can easily be read by anyone who intercepts it. This vulnerability to man-in-the-middle attacks and other types of cyber attacks puts sensitive information at risk.
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, is a variant of HTTP that adds an extra layer of security by encrypting the data transmitted between the client (usually a web browser) and the server. This encryption helps protect against man-in-the-middle attacks and other types of cyber attacks that could potentially compromise sensitive information.
To establish an HTTPS connection, the client and the server must first exchange SSL/TLS certificates to authenticate each other’s identities and establish an encrypted connection. The SSL/TLS certificate used by the server is typically issued by a trusted third-party certificate authority (CA), such as Let’s Encrypt or DigiCert.
Once the SSL/TLS certificate has been exchanged and the encrypted connection established, the client and the server can communicate securely using HTTPS. Any data transmitted between the client and the server is encrypted, making it much more difficult for anyone to intercept and read.
Advantages of HTTPS over HTTP
- Improved security: The main advantage of HTTPS is improved security. By encrypting the data transmitted between the client and the server, HTTPS helps protect against man-in-the-middle attacks and other types of cyber attacks that could potentially compromise sensitive information. This is especially important for websites that handle sensitive information, such as online stores or financial services websites.
- Enhanced credibility: Obtaining an SSL/TLS certificate can increase trust in your website among users and potential customers. When a user sees that your website is secured with an SSL/TLS certificate, they are more likely to feel confident that their personal information is safe and that your website is legitimate.
- Improved search engine rankings: Google and other search engines use SSL/TLS certificates as a ranking signal, so having an SSL/TLS certificate can help improve your search engine rankings. This is especially important if you want to attract more organic traffic to your website.
Disadvantages of HTTPS
While HTTPS has many advantages, there are also some potential disadvantages to consider:
- Cost: One potential disadvantage of HTTPS is the cost of obtaining an SSL/TLS certificate. While there are free SSL certificate options available from providers like Let’s Encrypt, paid SSL certificates can be more expensive, especially for multi-year or wildcard certificates that cover multiple subdomains.
- Performance overhead: Using HTTPS can also result in a slight performance overhead due to the additional processing required to establish and maintain the encrypted connection. This can be especially noticeable on websites with high traffic or complex content.
When to use HTTP vs HTTPS
So, when should you use HTTP and when should you use HTTPS? Here are a few factors to consider when deciding between these two protocols:
- Sensitive information: If your website handles sensitive information, such as passwords, financial data, or personal information, it’s important to use HTTPS to protect this information from potential cyber attacks.
- User trust: If you want to increase user trust in your website and boost credibility, using HTTPS can be a good choice. An SSL/TLS certificate can help show users that you are committed to protecting their privacy and security.
- Search engine rankings: As mentioned earlier, Google and other search engines use SSL/TLS certificates as a ranking signal. If you want to improve your search engine rankings and attract more organic traffic, using HTTPS can be a good option.
- Performance: If your website has high traffic or complex content, the performance overhead of HTTPS may be a concern. In this case, you’ll want to carefully weigh the benefits of HTTPS against the potential performance impact. In some cases, it may be worth investing in more expensive SSL/TLS certificates that offer faster performance or other performance enhancements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HTTPS is a more secure and trusted protocol than HTTP, offering improved security, enhanced credibility, and improved search engine rankings. However, HTTPS also has some potential disadvantages, including the cost of obtaining an SSL/TLS certificate and the performance overhead.
When deciding between HTTP and HTTPS, consider the needs and goals of your website. If your website handles sensitive information or you want to increase user trust and credibility, using HTTPS is a good choice. If your website has high traffic or complex content, carefully weigh the benefits of HTTPS against the potential performance impact.
Regardless of which protocol you choose, ensure that your website is as secure and trusted as possible. By protecting your website and your users’ sensitive information, you can build trust and credibility with your audience.
Got questions? Shot us a comment. Don’t forget to sign up for your newsletter for more security tips, great plugins and … wait for it … some great book tips!